Introduction

Jim F. Pearson photo
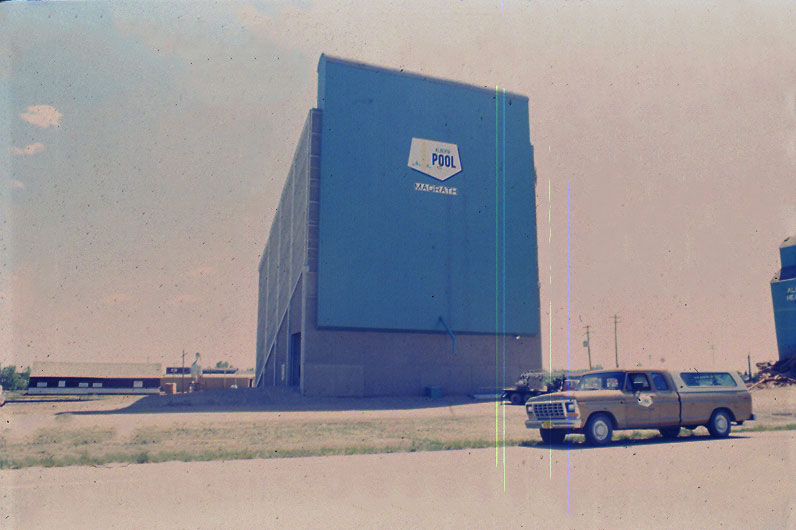
The concrete elevator seen here stands out as a unique example of Alberta’s ingenuity. For a time in the 1980s, it was the ‘Cadillac’ of the grain industry and the future of what was to come, replacing the iconic wooden grain elevators of old (and hopefully spread across Western Canada). The Buffalo-Sloped-Bin (BSB) 1000 series was the name of this futuristic design, created in collaboration between Alberta Wheat Pool (AWP) and Buffalo Engineering Ltd. Out of three examples built of this version, only two remain; one in Fort Saskatchewan and one in Magrath. The other elevator in Vegreville was demolished in 2009.
Background
From the early 1900s to the early 1980s, the wood grain elevator ruled the landscapes across western Canada. The late 1970s were good times for Alberta’s farmers and for one of the major western Canadian grain companies—Alberta Wheat Pool. A few years of bumper crops and high grain prices kept the wooden elevator network humming and added well to the profits of the Pool. With some of the surplus profit, AWP decided to do some design work with an engineer from Edmonton, by the name of Klaus “Nick” Drieger. Drieger and his company, Buffalo Engineering Ltd., drew up the initial concepts of the new concrete grain elevator to be built with large modular precast concrete pieces, sloped grain bins (to help with the grain flow) and clad with non-combustible pre-finished metal panels.
Read more